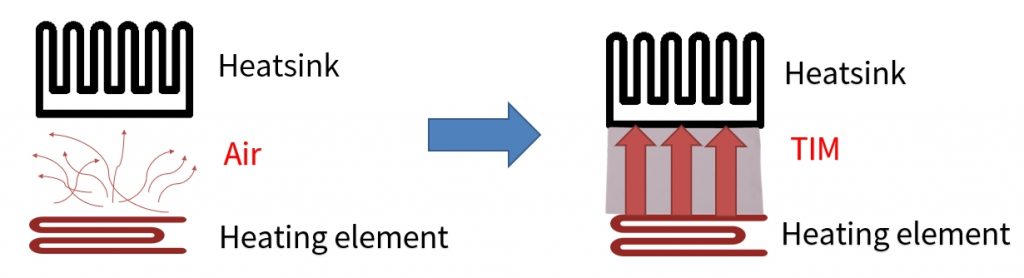
In the realm of electronics, efficient heat dissipation is critical to maintaining the performance and longevity of devices. Thermal Interface Materials (TIM) are at the forefront of this battle, acting as the unsung heroes that bridge the gap between heat-generating components and their heat sinks. Among the various types of TIMs, thermal pads and thermal paste are the most prevalent, often considered the key elements in optimizing heat transfer. These materials are designed to fill microscopic gaps and imperfections on the surfaces they connect, ensuring maximum thermal conductivity. Whether you’re using a thermal pad or thermal paste, the effectiveness of these TIMs can mean the difference between a well-functioning device and one that suffers from overheating.
Thermal pads are often favored for their ease of use. These pre-formed, solid pads are placed directly between the heat source and the heat sink, providing an efficient thermal path. They are particularly useful in applications where consistent pressure and uniform thickness are crucial, such as in laptops or small form-factor devices. The thermal pad is a versatile TIM solution, available in various thicknesses and materials to suit different thermal requirements. Despite their simplicity, thermal pads offer reliable performance and are often chosen for their durability and ease of application.
Thermal paste, also known as thermal grease, is a more traditional TIM solution that offers superior thermal conductivity when applied correctly. Unlike thermal pads, thermal paste is a viscous substance that requires careful application to avoid air bubbles, which can significantly reduce its effectiveness. However, when properly applied, thermal paste can outperform thermal pads, making it the preferred choice for high-performance computing applications, such as gaming PCs and workstations. Thermal paste is particularly effective in situations where the surfaces are not perfectly flat, as its fluid nature allows it to conform to the microscopic imperfections of the surfaces it contacts.
Thermal gel, which combines the best attributes of thermal pads and thermal paste. Thermal gel offers the convenience of a pad with the superior thermal conductivity of a paste. Its semi-solid form allows for easy application, similar to a thermal pad, while its high thermal conductivity makes it an excellent choice for demanding applications. Thermal gels are gaining popularity in industries that require both high performance and ease of use, bridging the gap between traditional thermal pads and paste.
Thermal interface materials(TIMs) cannot be overstated. As electronic devices continue to shrink in size while increasing in power, the demand for effective heat dissipation solutions will only grow. Whether it’s a thermal pad or thermal paste, choosing the right TIM is crucial for maintaining the performance and reliability of electronic devices. Engineers and designers must carefully consider the specific needs of their applications to select the most appropriate TIM. In many cases, a combination of different TIMs, such as using both a thermal pad and thermal paste, can provide the best results.
Thermal interface materials(TIMs) like thermal pads and thermal paste are vital components in the management of heat dissipation in electronic devices. These materials ensure that heat is efficiently transferred away from critical components, thereby enhancing performance and extending the lifespan of the device. As technology advances, the importance of selecting the right TIM will only become more critical, making thermal pads and thermal paste key players in the future of electronics.